Kell Blood Group
ScienceTopping | Sept 15, 2024
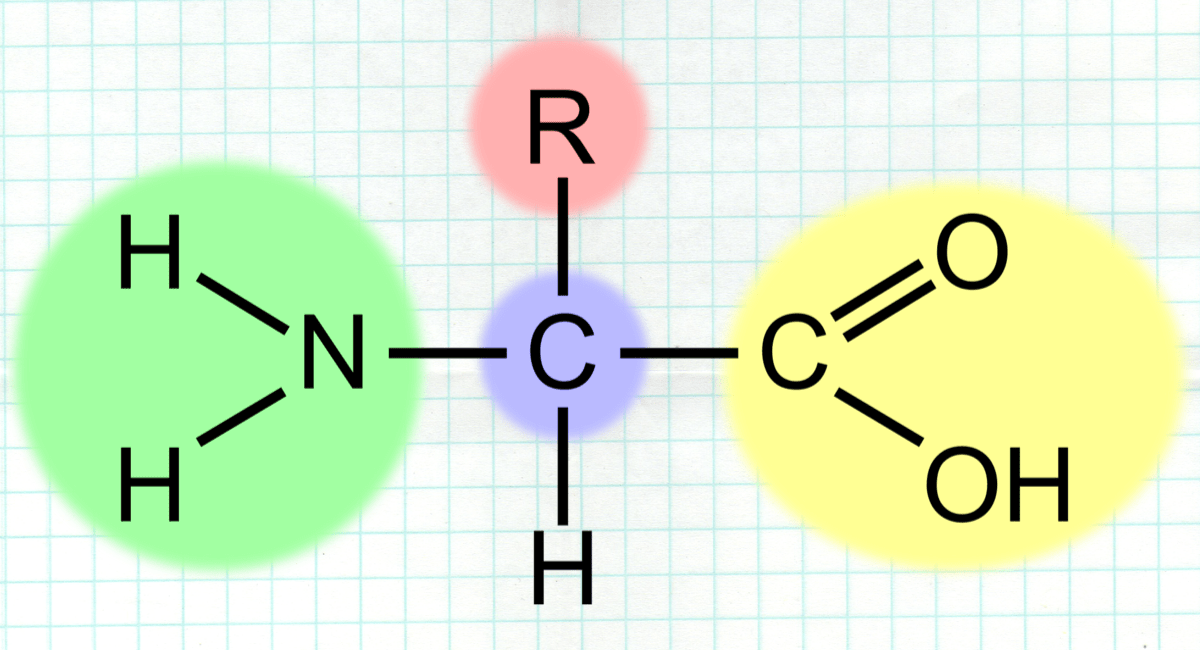
Tracing back to the molecular level, XK gene first produces Kx substance, which is
an important precursor for Kell antigen. In order to produce proper Kell antigens, KEL metallo-endopeptidase (KEL gene) located on chromosome 7 is the gene that converts Kx
substance into the proper functional Kell antigen. As the result of the polymorphic nature of KEL gene, 25 antigens may be manifested. Just any other
antigens on the red blood cells, Kell antigens are glycoproteins embedded in the membrane of red blood cells. Since there are 2 major antigens in Kell
blood group, there are 3 phenotypes in general, with K-k+ phenotype as the most common category.
Advertisement
The harm brought about by Kell antigens occurs during pregnancy and blood transfusion under special conditions, just like ABO and Rhesus antigens. First of all, when a Kell negative firstly preganant mother has a Kell positive baby, anti-K antibodies are produced if the baby's blood with Kell antigens mixes with the mother's blood with no Kell antigens, as Kell antigens are recognised as foreign substances to the mother's immune system. However, this still causes no harm to the first baby yet. In the second pregnancy, if the Kell negative mother has a Kell positive baby again, the previously sensitised mother will produce sufficient anti-K antibodies against the Kell antigens of baby's red blood cells. This is the deleterious haemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN).
As for haemolytic transfusion reactions (HTR), Kell negative individual can only receive Kell negative blood. Notwithstanding, Kell positive individual is allowed to receive either Kell positive or Kell negative blood.
McLeod neuroacanthocytosis syndrome typically manifests between 30 and 40 years of age, with the following common conditions.
- Cardiomyopathy
- Muscular dystrophy
- Psychiatric disturbances
- Neurological defects, such as loss of reflexes and movement disorders
For the symptomatic management of McLeod syndrome, dopamine-blocking agents such as tiapride and clozapine are used to reduce chorea.