ABO Blood Group
ScienceTopping | Sept 13, 2023
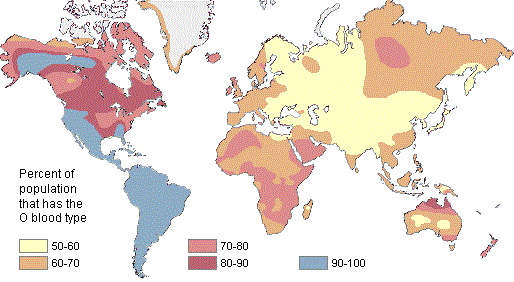
When doctors need to use blood packs
to save patients suffering from severe blood loss, blood groups of the patient must be matched with those of donors' blood packs. To be compatible,
patient with blood group A must receive blood from donor with blood group A or O only. If one's blood is not compatible with another person's
blood, agglutination will occur due to antibody-antigen binding, resulting in blood clot which can be fatal if not treated promptly.
Advertisement
Case Scenario 1:
A father has AB blood group. A mother has O blood group. What are the possible blood groups of their children?The father's genotype must be IAIB, as both allele are codominant, showing up in the genotype at the same time. Meanwhile, the mother's genotype must be IOIO, as the allele is autosomal recessive. An autosomal recessive gene can only be inherited when both of the recessive alleles are present in the genotype. Either IA or IB allele from the paternal side will be inherited in the child's genotype. From the maternal side, IO must be inherited in the genotype of their child. Thus, the following combinations are the possible genotypes of their children, giving rise to blood group A and B respectively.
- IAIO (50%)
- IBIO (50%)
Case Scenario 2:
A father has A blood group. A mother has B blood group. What are the possible blood groups of their children?The father's genotype may be IAIA or IAIO, as IA allele is dominant over IO. Meanwhile, the mother's genotype may be IBIB or IBIO. If the father's genotype is IAIA, then IA allele from the paternal side must be inherited in the child's genotype. If the father's genotype is IAIO, then either IA or IO allele from the paternal side will be inherited in the child's genotype. From the maternal side, if the mother's genotype is IBIB, then IB allele must be inherited in the child's genotype. If the mother's genotype is IBIO, then either IB or IO allele from the maternal side will be inherited in the child's genotype. Thus, the following combinations are the possible genotypes of their children, giving rise to blood group A, B, O and AB respectively.
- IAIO (25%)
- IBIO (25%)
- IOIO (25%)
- IAIB (25%)
Advertisement
Meanwhile, the red blood cells in blood group O contain anti-A and anti-B antibodies without A and B antigens, thus regarded as the universal donor blood group. This is because there is no antigen in the donor to react with anti-A or anti-B antibodies in blood group A and B. On the other hand, the red blood cells in blood group AB contain both A and B antigens without anti-A and anti-B antibodies, thus regarded as the universal recipient blood group. This is because there is no antibody in the recipient to react with A or B antigens in A, B or AB blood group. It is important to recognise the different locations of the A and B antigens as well as anti-A and anti-B antibodies, which are crucial for comprehending the logics behind antigen-antibody binding in different blood group.
- A and B antigens are on red blood cells' surface.
- Anti-A and anti-B antibodies are in blood plasma.
Advertisement
Problems occur when blood incompatibility happens during blood transfusion. If blood in blood group A is used for blood transfer to a recipient with blood group B, anti-A antibodies in the recipient's blood plasma will be bound by A antigens in blood pack used, resulting in blood agglutination or blood clotting. Consequently, blood circulation in the recipient will be interrupted because blood cannot flow through the blood clots formed around the region of blood transfusion. From this case, the importance of blood group labelling can clearly be seen. Get a free instant blood group test now!